Output Format Specifiers
Contents
Test Environments
| Hardware Comments | Nut/OS 4.6.4 |
Nut/OS 4.7.4 |
Nut/OS 4.8.0 |
Nut/OS 4.8.7 | |
| Ethernut 1.3 H | No output of Double Binaries |
No output of Double Binaries |
No output of Double Binaries |
No output of Double Binaries Compiler: AVR-GCC 4.3.2 | |
| Ethernut 2.1 B | No output of Double Binaries |
No output of Double Binaries |
No output of Double Binaries |
No output of Double Binaries Compiler: AVR-GCC 4.3.2 | |
| Ethernut 3.0 E | OK Binaries |
NO | OK Binaries |
||
| EIR 1.0 C | Set jumper JP1 to DEBUG mode. |
OK Binaries |
NO | OK Binaries |
|
| Compiler: ARM-GCC 4.2.2 ; AVR-GCC 4.3.0 | |||||
Description
On this page you will learn about the different format specifiers of the printf() function.
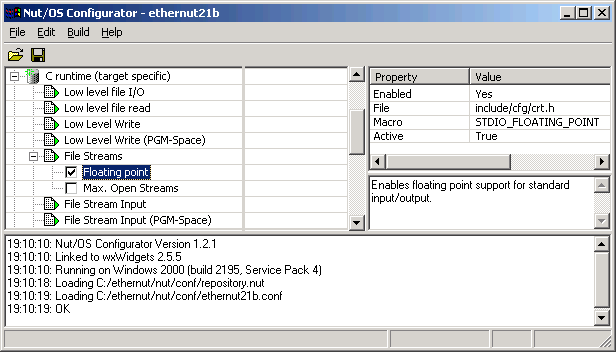
Note that you have to activate floating point numbers in the Nut/OS configurator in order to use them.
Format Specifiers
| Format Specifier |
Data type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| <source lang="c">%d</source> | Int (Integer) | 161 |
| <source lang="c">%c</source> | Character | a |
| <source lang="c">%f</source> | Floating-point number (Holds a total of 7 digits) |
3.141592 |
| <source lang="c">%lf</source> | Double (long floating) (Holds a total of 16 digits) |
3.141592653589793 |
| <source lang="c">%s</source> | String | abcdef |
| <source lang="c">%x</source> | Hexadecimal | A1 |
Source Code
<source lang="c">
- include <dev/board.h>
- include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
unsigned long baud = 115200;
NutRegisterDevice(&DEV_DEBUG, 0, 0);
freopen(DEV_DEBUG_NAME, "w", stdout);
_ioctl(_fileno(stdout), UART_SETSPEED, &baud);
unsigned int integf = 161;
float floatf = 3.141592;
double doublef = 3.141592653589793;
char characf = 'a';
char *stringf = "abcdef";
printf("Integer:\n\n");
printf("%d|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%d)\n", integf);
printf("%9d|\t\t(format specifier: %%9d)\n", integf);
printf("%09d|\t\t(format specifier: %%09d)\n", integf);
printf("%-9d|\t\t(format specifier: %%-9d)\n", integf);
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Floating:\n\n");
printf("%f|\t\t(format specifier: %%f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%1.2f|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%1.2f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%1.6f|\t\t(format specifier: %%1.6f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%1.8f|\t\t(format specifier: %%1.8f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%8.1f|\t\t(format specifier: %%8.1f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%8.3f|\t\t(format specifier: %%8.3f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%-8.3f|\t\t(format specifier: %%-8.3f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%08.3f|\t\t(format specifier: %%08.3f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Double: (long Floating)\n\n");
printf("%lf|\t\t(format specifier: %%lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%1.2lf|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%1.2lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%1.6lf|\t\t(format specifier: %%1.6lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%1.15lf|\t(format specifier: %%1.15lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%15.1lf|\t(format specifier: %%15.1lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%15.3lf|\t(format specifier: %%15.3lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%-15.3lf|\t(format specifier: %%-15.3lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%015.3lf|\t(format specifier: %%015.3lf)\n", doublef);
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Character:\n\n");
printf("%c|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%c)\n", characf);
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("String:\n\n");
printf("%s|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%s)\n", stringf);
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Hexadecimal:\n\n");
printf("%d|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%d)\n", integf);
printf("%x|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%x)\n", integf);
printf("%X|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%X)\n", integf);
for(;;); return 0;
}
</source>
Details
<source lang="c">
unsigned int integf = 161; float floatf = 3.141592; double doublef = 3.141592653589793; char characf = 'a'; char *stringf = "abcdef";
</source>
At first we declare a number of variables and a pointer which will later be formatted and displayed by the format specifiers within printf statements.
<source lang="c">
printf("Integer:\n\n");
printf("%d (format specifier: %%d)\n", integf);
printf("%9d (format specifier: %%9d)\n", integf);
printf("%09d (format specifier: %%09d)\n", integf);
printf("%-9d (format specifier: %%-9d)\n", integf);
</source>
As you can see in the output section, %d displayes an integer value without any spaces in front of.
This specifier can be modified by entering numbers between the % and the d
By using %9d the integer value takes at least 9 spaces for itself. If the value has less than 9 digits, the spaces getfilled by blanks.
If you use %09d instead the spaces gets filled by zeros.
This is called Minimum Field Width.
Putting a - (Minus) in front of the Minimum Field Width value causes the output to be justified on the left.
<source lang="c">
printf("Floating:\n\n");
printf("%f|\t\t(format specifier: %%f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%1.2f|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%1.2f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%1.6f|\t\t(format specifier: %%1.6f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%1.8f|\t\t(format specifier: %%1.8f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%8.1f|\t\t(format specifier: %%8.1f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%8.3f|\t\t(format specifier: %%8.3f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%-8.3f|\t\t(format specifier: %%-8.3f)\n", (double)floatf);
printf("%08.3f|\t\t(format specifier: %%08.3f)\n", (double)floatf);
</source>
The specifier for floating point numbers %f may be customized as well.
%1.6f for example sets the Minimum Field Width to 1 and the Precision Specifier to 6. This is the number of decimal places.
Note that the statements using %f and %1.6f look the same. Thats because %f uses a default decimal places (Precision) value of 6, as %1.6f does.
When using more than 7 digits, e.g. %1.7f (1+7=8), as only 7 digits are supported, the additional ones hold random numbers. (See line 5)
<source lang="c">
printf("Double: (long Floating)\n\n");
printf("%lf|\t\t(format specifier: %%lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%1.2lf|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%1.2lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%1.6lf|\t\t(format specifier: %%1.6lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%1.15lf|\t(format specifier: %%1.15lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%15.1lf|\t(format specifier: %%15.1lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%15.3lf|\t(format specifier: %%15.3lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%-15.3lf|\t(format specifier: %%-15.3lf)\n", doublef);
printf("%015.3lf|\t(format specifier: %%015.3lf)\n", doublef);
</source> <source lang="c">
printf("Character:\n\n");
printf("%c|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%c)\n", characf);
</source> <source lang="c">
printf("%s|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%s)\n", stringf);
</source> <source lang="c">
printf("Hexadecimal:\n\n");
printf("%d|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%d)\n", integf);
printf("%x|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%x)\n", integf);
printf("%X|\t\t\t(format specifier: %%X)\n", integf);
</source>
Note that the last two printf statements use the same int variable as the first one does. By using the %x specifier, the decimal number gets automatically converted into the hexadecimal system.
Output
Output with Nut/OS 4.6.4 on Ethernut 3.0 E:
Integer:
161| (format specifier: %d)
161| (format specifier: %9d)
000000161| (format specifier: %09d)
161 | (format specifier: %-9d)
----------------------------------------------------
Floating:
3.141592| (format specifier: %f)
3.14| (format specifier: %1.2f)
3.141592| (format specifier: %1.6f)
3.14159203| (format specifier: %1.8f)
3.1| (format specifier: %8.1f)
3.142| (format specifier: %8.3f)
3.142 | (format specifier: %-8.3f)
0003.142| (format specifier: %08.3f)
----------------------------------------------------
Double: (long Floating)
3.141593| (format specifier: %lf)
3.14| (format specifier: %1.2lf)
3.141593| (format specifier: %1.6lf)
3.141592653589793| (format specifier: %1.15lf)
3.1| (format specifier: %15.1lf)
3.142| (format specifier: %15.3lf)
3.142 | (format specifier: %-15.3lf)
00000000003.142| (format specifier: %015.3lf)
----------------------------------------------------
Character:
a| (format specifier: %c)
----------------------------------------------------
String:
abcdef| (format specifier: %s)
----------------------------------------------------
Hexadecimal:
161| (format specifier: %d)
a1| (format specifier: %x)
A1| (format specifier: %X)
See also
- More Nut/OS Examples
External Links
[1] Wikipedia article about the printf function".